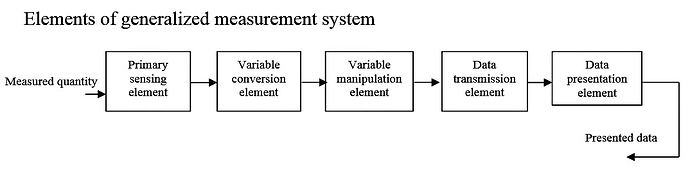
Instrumentation is the process of measuring, calibrating, and controlling the physical variable such as pressure, flow, temperature etc using a instrument.
Calibration
Calibration is the process of checking the accuracy and correctness of an instrument by comparing it with a standard instrument.
Accuracy
The degree of closeness to the true value.
Error
The deviation of the true value from the desire value.
Transducers
Transducer is defined as a device that receives energy from one system and transmits it to another often in a different form. Basically there are two types of transducers:
-
Electrical Transducers -
Mechanical Transducers
An electrical transducer gives a sensing device by which the physical, mechanical, optical quantity to be measured, is transformed directly by a suitable mechanism into an electrical signal.
Electrical transducers can be classified into two ways:
-
Active Transducers -
Passive Transducers
Active Transducers
Active transducers generate an electrical signal directly in response to the physical parameter and does not require external power source for its operation. Active transducers are self generating devices which operate under energy conversion principle and generate an equivalent output signal.
Passive Transducers
Passive transducers operate under energy controlling principle which makes it necessary to use an external electrical source with them. They depend up on the change in an electrical parameter (R, L, C).
E.g. Strain Gauge, Thermistors
Selecting a Transducers
Following should be considered while selecting a transducer:
-
Operating range -
Sensitivity -
Environmental compatibility -
Accuracy