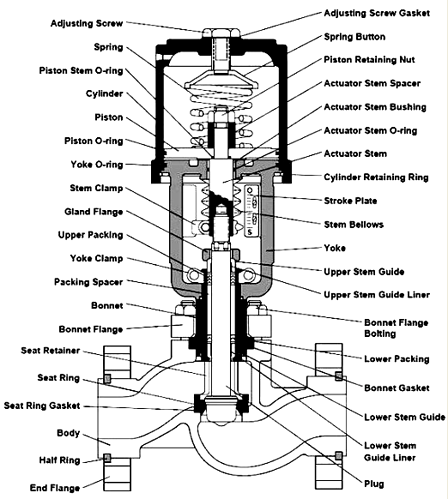
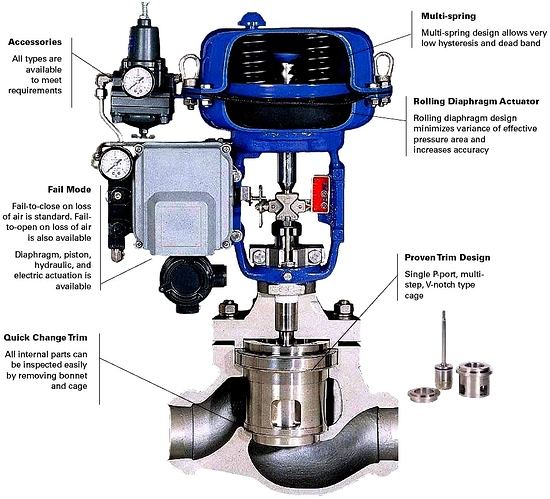
Valve body:
It is a housing for internal valve parts having inlet and outlet flow connection.
It serves as the principal element of a valve assembly because it is the framework that holds everything together.
The body, the first pressure boundary of a valve, resists fluid pressure loads from connecting piping. It receives inlet and outlet piping through threaded, bolted, or welded joints.
Trim:
The parts (except the body) of control valve that comes into contact with the flowing fluid is known as Trim. The internal elements of a valve are collectively referred as a valve trim.
The trim typically includes a disk, seat, stem, and sleeves needed to guide the stem. The performance of valve is determined by the disk and seat interface.
Stem:
It is a rod extending through the bonnet assembly to permit the positioning the valve plug.
Stems are typically forged and connected to the disk by threaded or welded joints. For valve designs requiring stem packing or sealing to prevent leakage, a fine surface finish of the stem in the area of the seal is necessary. Typically, a stem is not considered a pressure boundary part.
Plug:
It is the movable part, which provides variable restriction in a port.
Cage:
A part of a valve trim that surrounds the closure member and may provide flow characterization and/ or a seating surface.
It may also provide stability, guiding, balance, and alignment, and facilitate assembly of other parts of the valve trim.
Seat:
It is the portion of the valve, which a valve plug contact for closure.
The seat or seal rings provide the seating surface for the disk. In some designs, the body is machined to serve as the seating surface and seal rings are not used. In other designs, forged seal rings are threaded or welded to the body to provide the seating surface.
Bonnet:
The cover for the opening in the valve body is the bonnet.
In some designs, the body itself is split into two sections that bolt together. Like valve bodies, bonnets vary in design. Some bonnets function simply as valve covers, while others support valve internals and accessories such as the stem, disk, and actuator.
Actuator.
An actuator is a pneumatic hydraulic, or electrically powered device which supplies force and motion to open or close a valve.