The PID controller Loop Simulator software is used to interact with and tune simulated process control loops.
The simulator mimics various processes, controller options, disturbances, and control valve issues.
This real-time simulator clearly and effectively demonstrates the essentials of process dynamics, PID controllers, control loop tuning, and more.
It is supplemented with a comprehensive set of step-by-step practical exercises to guide you through many aspects of controller tuning and loop performance, while you gain first-hand experience on life-like control loop simulations.
Loop Simulator
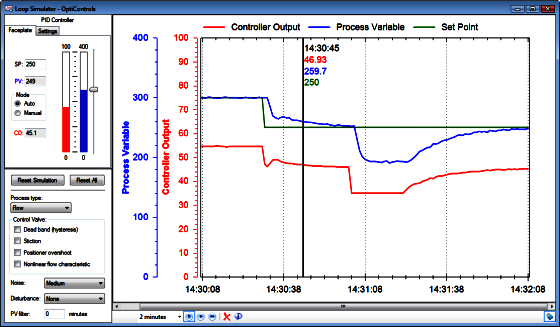
Simulation Features
- The real-time chart with trends of process variable, controller output, and set point shows controller and process responses.
- Run the simulation in real-time to get that plant-like experience, or in fast-forward mode to minimize simulation time.
- Pause the simulation to take measurements from static trends.
- Select different X-axis time spans to narrow in on areas of interest, or scroll back in time or see past test data.
- Scale the Y-axis to narrow in on trends and see subtle response details.
- Use the vertical cursor-line to easily take measurements from your test data.
- Reset the process simulation (PV, SP, CO), or reset all settings to return the simulation to different starting conditions.
Process Simulation
- Choose from flow, temperature, tank level, conveyor, or steam drum level processes to gain experience with distinctly different types of dynamic process behavior.
- Simulate valve dead band (hysteresis), stiction, positioner overshoot and nonlinear flow characteristic to see how loop performance is affected by control hardware.
- Simulate various levels of measurement noise, and step-up, step-down, or random-walk disturbances to test how your tuning settings hold up under these adverse conditions.
- Apply a process variable filter to deal with measurement noise and see its effects on control loop response.
Controller Simulation
- Get visual feedback from the operator-type faceplate with bar-graphs and numeric readouts.
- Use slider bars for quickly changing set point or controller output, and numeric inputs for entering precise values.
- Simulate P, PI, or PID controllers and change tuning parameters to see their effects on the control loop and to try different tuning methods.
- Select from noninteractive, interactive, and parallel controller algorithms to simulate various brands of controllers.
- Choose whether proportional and derivative should work on set point or process variable, and/or choose set point filtering to learn the control improvements available from these options.
Practical Exercise Topics
- Process Types
- Characteristics of a Self-Regulating Process
- Characteristics of an Integrating Process
- Dead time and Settling time
- Small Lags and Dead Time
- Proportional Control
- Proportional + Integral Control
- Proportional + Integral + Derivative Control
- Controller Algorithms
- Proportional and Derivative on Error or Process Variable
- Set Point Filtering
- Process Variable Filtering
- Ziegler-Nichols Ultimate Cycle Tuning
- Ziegler-Nichols Tuning for Self-Regulating Processes
- Ziegler-Nichols Tuning for Integrating Processes
- Cohen-Coon Tuning and the PID Calculation Spreadsheet
- Lambda Tuning
- Tuning Control Loops with Long Dead Times
- Control Valve Dead Band
- Control Valve Stiction
- Positioner Overshoot
- Valve Characteristics
System Requirements
- Microsoft Windows XP, 7, 8, 8.1, 10
- Microsoft .Net Framework V2.0 or later
- Adobe PDF Reader for User Guide and Practical Exercises