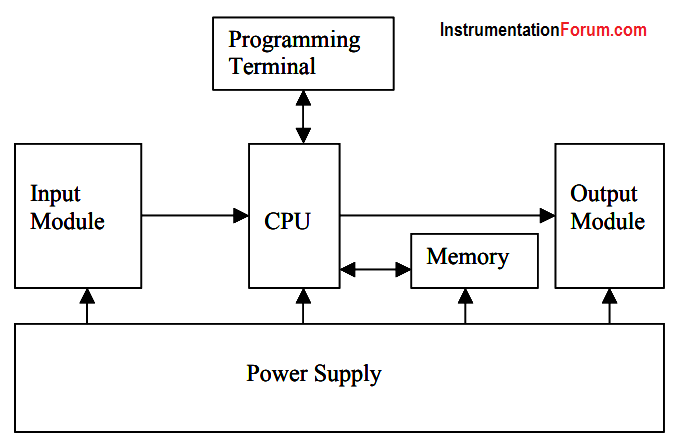
Like other computerized devices, there is a Central Processing Unit (CPU) in a PLC. The CPU, which is the “brain” of a PLC, does the following operations:
Updating inputs and outputs
This function allows a PLC to read the status of its input terminals and energize or deenergize its output terminals.
Performing logic and arithmetic operations
A CPU conducts all the mathematic and logic operations involved in a PLC.
Communicating with memory
The PLC’s programs and data are stored in memory. When a PLC is operating, its CPU may read or change the contents of memory locations.
Scanning application programs
An application program, which is called a ladder logic program, is a set of instructions written by a PLC programmer. The scanning function allows the PLC to execute the application program as specified by the programmer.
Communicating with a programming terminal.
The CPU transfers program and data between itself and the programming terminal.
A PLC’s CPU is controlled by operating system software. The operating system software is a group of supervisory programs that are loaded and stored permanently in the PLC’s memory by the PLC manufacturer.