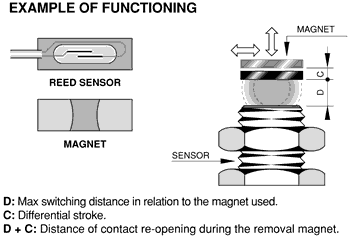
Magnetic proximity sensors are actuated by the presence of a permanent magnet. Their operating principle is based on the use of reed con-tacts, whose thin plates are hermetically sealed in a glass bulb with inert gas. The presences of a magnetic field makes the thin plates flex and touch each other causing an electrical contact.
Magnetic proximity sensor
The plate’s surface has been treated with a special material par-ticularly suitable for low current or high inductive circuits. Magnetic sensors compared to traditional mechanical switches have the following advantage:
-
Contacts are well protected against dust, oxidization and corrosion due to the hermetic glass bulb and inert gas; contacts are activated by means of a magnetic field rather than mechanical parts
-
Special surface treatment of contacts assures long contact life
-
Maintenance free
-
Easy operation
-
Reduced size
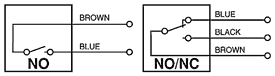
Outputs:
When using the NO (normally open) type the open reed contact closes as the magnet approaches. NO Magnetic sensors are two wires. When using the NO+NC type both NO (normally open) and NC (normally closed) functions are made available by means of a single glass bulb. NO+NC Magnetic sensors are supplied with three wires, one is in common, one is NO and one is NC
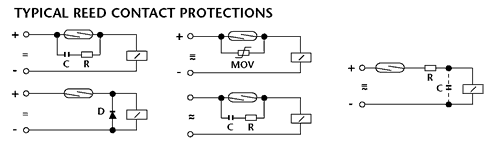
TYPICAL REED CONTACT PROTECTIONS
The lifespan of a magnetic sensor at low values of voltage and current depends on the mechanical characteristics of the contact while for higher values the operating life depends on the characteristics of the load. In these cases, it is suggested to apply some form of external protection at the sensor output.
SWITCHING POWER DIAGRAM
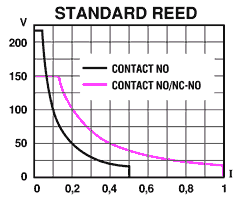
Voltage (V), switching current (I) and max. power § mean the max. switching istantaneous value in presence of loads. When choosing a type of contact it is recommended that the following formula be applied: P = V x I.