Summary of Valve Types covers globe valve, needle valve, ball valve, gate valve, plug valve, check valve, butterfly valve, non-return valve, pressure relief valve.
Summary of Valve Types
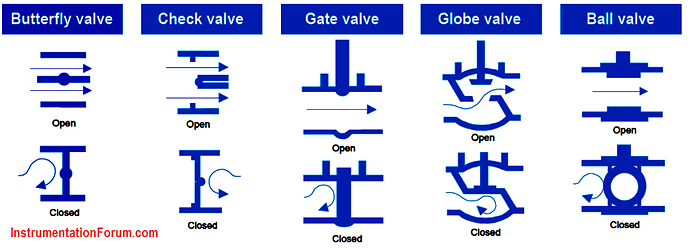
Globe valve
• Suitable for regulating flow
• Tight shut-off
• Pressure drop when open
• Used for high pressure clean fluids
Needle valve
• Suitable for regulating flow
• Fine control in small diameter piping
• Tight shut-off
• Used for clean fluids that have low flows
• High pressure drop when open
Ball valve
• Not suitable for regulating flow except in some specialized ball valves
• Tight shut-off
• Low pressure drop when open
• Used for gas, liquids or slurries
Butterfly valve
• Suitable for regulating flow
• Not suitable for tight shut-off
• Low pressure drop when open
• Used for low line pressure and large pipe line diameters
• Wide range of service: gas, liquids and slurries
Gate valve
• Not suitable for flow regulation, only suitable for on or off
• Tight shut-off
• Low pressure drop when open
Diaphragm valve
• Suitable for on/off or narrow range throttling control
• Tight shut-off
• Low pressure drop when open
• Used for corrosive fluids and slurries
Plug valve
• Suitable for regulating flow
• Tight shut-off
• Quick opening
• High pressure drop when open
Non-return valve
• Allow flow in one direction only
• Self closing
• Low pressure drop when open
• Not suitable for reciprocating pump discharge
Pressure relief valve
• Opens at pre-determined pressure level