SCADA is an acronym for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. This presents the data as a viewable and controllable system on the screen of a computer.
The data thus collected can be stored and analysed for optimization of the process and for better real time process control.
It assists plant-operating personnel by monitoring and announcing abnormal conditions and failure of equipment.
It allows the operators to perform calculations based on the sensor inputs. Daily, weekly, monthly reports can be prepared using the stored data.
It also allows the operator to know the state of a process by an alarm associated with it.
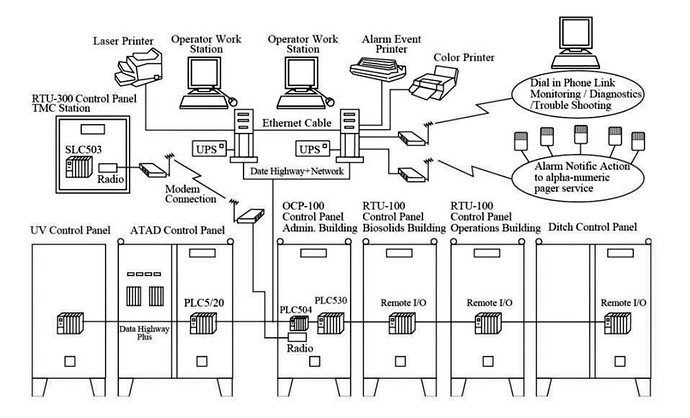
A typical SCADA is shown in Figure.
SCADA System
Source: Kruger
Figure: Typical SCADA communication overview
Monitoring and Control Equipment
For maximum use and effectiveness, signals generated by various sensors and instruments are transmitted from the sensor to a receiver installed at another location.
Often, the sensor output is transmitted to a control panel or computer system, which allows operators to inspect many process variables simultaneously.
The three components of a signal-transmission system are the transmitter, receiver and transmission medium (the connection between the transmitter and receiver).
The transmitter converts a mechanical or electrical signal from the sensor into a form that the transmission medium can use.
The transmission medium contains the signal and transfers it to the receiver. The receiver subsequently converts it into a form that the receiving system can use.