I need exact application for the Pressure Gauge Syphons. I have already searched so many theories regarding that, some says it’s for pressure protection.
I am not getting how. Some says for temperature protection, by what degrees of temperature would that gauge be protected how to judge it & does that really bring down temperature to that extent that gauge stays protected. I need proper explanation for the same if anybody could guide me.

3 Likes
Pressure gauge siphons are used to protect the pressure gauge from the effect of hot pressure media such as steam and also to reduce the effect of rapid pressure surges. The pressure medium forms a condensate and is collected inside the coil or pigtail portion of the siphon. The condensate prevents the hot media from coming in direct contact with the pressure instrument. When the siphon is first installed, it should be filled with water or any other suitable separating liquid.
It can also be used to reduce the potentially damaging effects of rapid pressure changes. These low-cost devices allow systems builders to use a pressure sensor with a much lower temperature range in high-temperature applications.
Forms
Pigtail syphon
Coil syphon
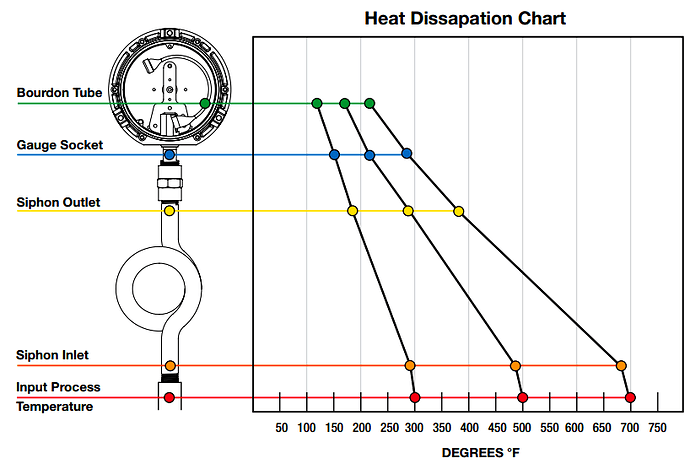
Pressure Gauge Siphon Heat Dissipation Chart
Different types of Pressure gauge siphons available in the market. As per our operating temperature, the Siphon’s shape, size, material, and other factors will change. Instrumentation vendors suggests the suitable siphon.
From the below example chart, the pressure gauge siphon acts as a thermal barrier between the process media and pressure gauge.
Note: The chart specifications will change based on the type of pressure gauge siphon. The below chart displays the readings for 3 different siphons.
These graphs represents the heat dissipation based on results of a specific laboratory test. These results may vary in the field based on multiple factors such as ambient temperature, type of process media and/or velocity. This data set is to be used as a reference point only. These test results are based on an ambient temperature of 68°F.
References: wika, Ashcroft
5 Likes
Excellent sir, that chart helped me a lot in clearing basics. Thankx again
What if the pressure medium changes it’s properties by ambient temperature changes? There would be definitely change in pressure showing inaccurate results, can anybody help me in this regards??
2 Likes
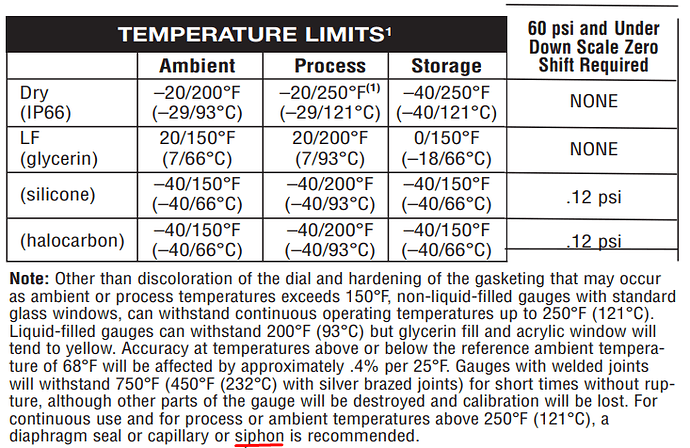
That’s why every instrument have the datasheet which defines maximum and minimum operating conditions. Also applicable process media pressure and temeprature ranges.
If any instrument operates outside of its allowable operating criteria, there will be considereable amount of accuracy loss in the measurement.
It applies to all instruments.
So we have to make sure to use the instrument as per its design.
In case the process media changes then we have to change our instrument too, if the max and min operating ranges changes or other factors.
2 Likes
Is there any sheet specifying range as per media.
1 Like
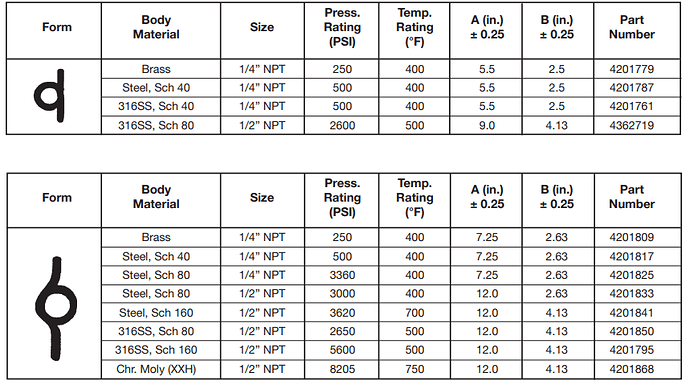
Example for process media.
Pressure Gauge Siphon Datasheet example
4 Likes


 Really Grt!! thankx
Really Grt!! thankx 